Uses of Augmented Reality in Healthcare Education
- Posted on August 31, 2022
- By Happy Kumari
- Read 5 minutes
Education is always divided into two parts: theory and practice. Whatever you learn, there will come a time when you must move away from textbooks, videos, instructor explanations, and demonstrations and into doing something with your own hands. Healthcare education is no exception in this context. Medical students spend years learning and practicing their skills before becoming doctors. At the same time, healthcare is distinct from other fields because it deals with something that is both complex, unpredictable, and fragile – the human body. Traditionally, healthcare students have practiced with various models and manikins resembling human bodies, parts, and organs, as well as cadavers used to train various medical skills. Students are allowed to perform treatments and surgeries on real patients as their education progresses, often under the supervision of experienced doctors. While such practice is quite effective, it is not without drawbacks. There are no models that can simulate the functioning of the human body and its organs. Due to the possibility of errors, practicing with patients can be dangerous. Patients may also be concerned about receiving treatment from inexperienced young doctors.
Fortunately, we live in a time when technology can frequently replace or recreate real life. Augmented reality (AR), in which virtual objects overlay the real world, has become an excellent training tool, with particular applications in healthcare education.
AR allows students to practice on virtual objects that closely resemble human bodies and organs without putting their patients’ health at risk. Many medical schools are already using augmented reality technology in a variety of ways. Consider the following examples of augmented reality applications for healthcare education.
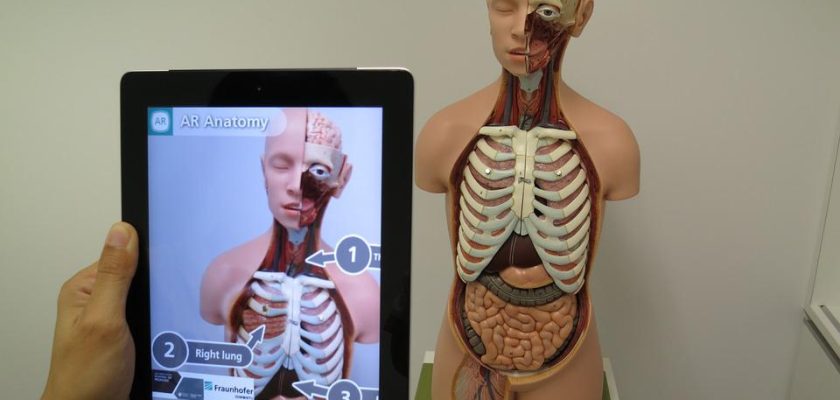
Using Augmented Reality To Learn Anatomy
Human anatomy practice in AR is becoming more common in medical schools. Students can view the human body in augmented reality rather than physical cadavers or plastic models. Furthermore, AR apps can show the parts and organs in motion, allowing students to see how they work. When used for anatomy studies, augmented reality can take several forms:
Displaying supporting data over physical models or text:
A plastic skeleton can be outfitted with QR codes or other markers that will activate AR text containing bone names, characteristics, functions, and other pertinent information. In augmented reality, a picture of a human heart with an AR marker can generate an animated 3D model of the same heart showing how it beats.
Markers are used to display 3D models:
Medical students, for example, can see a human skull with all of its individual bones in AR. The 3D model can be animated or interactive, depending on the complexity of the AR app. Students, for example, can “remove” bones and study them from all angles, or see inside the body. Such AR apps can recreate entire bodies, with each part or organ interactable.
Learning anatomy becomes much easier and more effective with AR. Getting an AR app may be less expensive for medical schools than providing enough models, specimens, and cadavers. AR learning provides students with greater flexibility because they can conduct their “labs” almost anywhere and at any time. In AR, any exercise can be repeated as many times as necessary to ensure the highest level of knowledge.
Using Augmented Reality to Practice Surgery
Practice is extremely important for surgeons. Much is dependent on movement precision and “muscle memory.” At the same time, setting up a surgical practice can be difficult. Practicing with real patients is fraught with danger, and not all patients agree to it. Although practicing on cadavers can naturally improve precision and fine movements, they cannot simulate the state of operating on a living body. Augmented reality can help in this situation. The AR application creates the illusion of performing surgery on a living organism by superimposing the animated image on a manikin.
While such practice provides a realistic experience, it poses no risk to patients. AR apps that use special headsets like Microsoft Hololens are an excellent learning tool for young surgeons. Students can use different scenarios to practice various surgeries and other procedures in augmented reality and see how the virtual “patient” reacts to their actions. With augmented reality, students can learn from their mistakes in the literal sense of the word without fear of endangering their patients’ lives or health. Naturally, each scenario in AR can be repeated as many times as necessary for the student to gain confidence in their surgical skills.
Remote Mentor Assistance Is Available During Emergency
Victims of accidents in remote areas are frequently treated first by paramedics, volunteers, or other emergency response personnel who may lack first-aid experience. Furthermore, in such cases, there is frequently insufficient time to transport the patient to the clinic or wait for qualified assistance. Life-saving activities must be carried out immediately and as quickly as possible. When emergency response units are outfitted with augmented reality headsets and applications, they can treat accident victims while under the supervision of experienced doctors who may be thousands of miles away.
The AR headset projects an image of the patient onto the display of the remote doctor, who can then give oral or graphic instructions on how to stabilize the patient on the spot. The doctor can add images to the screen that will be projected back to the accident site and superimposed on the patient in their headset view. Using augmented reality, the team ensures that the patient receives the most effective first aid care, that the appropriate instruments are used, and that all procedures are performed as accurately as possible.
The Primary Advantages of Augmented Reality in Healthcare Education
Our brief examination of the potential applications of augmented reality in healthcare education reveals the following advantages of using the technology:
Realistic encounter: AR creates life-like virtual objects that provide the most realistic impression of how the human body is constructed and functions.
Low danger and high safety: When compared to practicing on real patients, augmented reality training involves much less risk for the patient, instilling much more confidence in the student.
Cost-effectiveness: While sophisticated AR apps can be costly to develop, they are relatively inexpensive in comparison to the cost of setting up anatomy theaters and providing cadavers and specimens for students to practice on.
Increased efficiency: Students can practice as much and as frequently as they want with AR apps. Unlike practicing in laboratories, where students must rely on the schedule and the availability of disposable materials, AR training can ensure better results in training the necessary skills.
Expert assistance is available: Augmented reality apps make it simple to connect trainees or remote workers with mentors or experts who can provide real-time instructions or assistance.
Augmented reality is a powerful educational tool that is well-known for its ability to recreate virtual training scenarios in real-world scenarios. Its effectiveness in healthcare is based on the ability to improve doctors’ skills without putting patients at risk.
